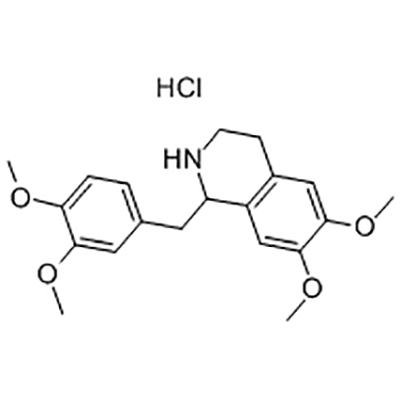
factory customized Membrane Water Treatment - Tetrahydropapaverine hydrochloride – JIN DUN
factory customized Membrane Water Treatment - Tetrahydropapaverine hydrochloride – JIN DUN
factory customized Membrane Water Treatment - Tetrahydropapaverine hydrochloride – JIN DUN Detail:
Tetrahydropapaverine hydrochloride is used as the intermediate of Cisatracurium besylate .
Cisatracurium besylate is the benzene sulfonate salt form of atracurium. It is a kind of artificially synthetic non-depolarizing muscle relaxants with its role similar as tubocurarine. It has an onset time of 1 minute and duration time of 15 minutes. The treatment dose does not affect the heart, liver and kidney function. It also has no accumulation property. It also can induce the release of histamine when used at large doses. For muscle relaxation or breathing control required in surgery, compared with current clinical major muscle-relaxing anesthetic drugs, cisatracurium besylate is not metabolized through liver or kidney, and has cardiovascular stability; its effect of muscle relaxation is 3 times as strong as atracurium without any cardiovascular side effects. Cisatracurium besylate is mainly applied to general anesthesia, and can be widely used in intubation, treating liver and kidney dysfunction, used in cardiovascular surgery and elderly and pediatric patients.
Compared with atracurium, this product has no dose-dependent adverse effects of histamine release; however, the disadvantage is that patients with liver and kidney dysfunction should administrate with caution.
Since 1996 for the first time when this drug has entered into market in UK, foreign countries have gradually applied it to replace vecuronium and atracurium as the mainstream of clinical muscle relaxants.
Product detail pictures:
Related Product Guide:
Assume full accountability to fulfill all demands of our purchasers; attain continual advancements by marketing the advancement of our clientele; grow to be the final permanent cooperative partner of purchasers and maximize the interests of purchasers for factory customized Membrane Water Treatment - Tetrahydropapaverine hydrochloride – JIN DUN , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Yemen, Bangalore, Hamburg, We take measure at any price to attain essentially the most up-to-date gear and procedures. The packing of nominated brand is our a further distinguishing feature. The solutions to assure years of trouble-free service has attracted a great deal customers. The goods are obtainable in improved designs and richer variety, they're produced scientifically of purely raw supplies. It accessible in a variety of designs and specifications for the selection. The newest forms are much far better than the previous one and they're extremely popular with several clients.
A nice supplier in this industry, after a detail and careful discussion, we reached a consensus agreement. Hope that we cooperate smoothly.


![Factory Free sample Water Neutralizer System - 4-[4-[(5S)-5-(Aminomethyl)-2-oxo-3-oxazolidinyl]phenyl]-3-morpholinone Hydrochloride – JIN DUN](https://cdn.globalso.com/jindunchem-med/dc3948321.jpg)
![Hot Selling for Commercial Water Filtration Systems - 2-butyl-5-nitro-3-benzofuranyl)[4-[3-(dibutylaMino)propoxy]phenyl] – JIN DUN](https://cdn.globalso.com/jindunchem-med/922e79ba.jpg)